Is Your Scheduled Job Actually Stuck?
Have you ever opened your Apex Jobs page and felt that mini-panic when you see a Salesforce batch job queued for hours? It looks like the system is just ignoring your code. I’ve seen teams waste hours trying to “fix” a job that wasn’t even broken in the first place. But here’s the thing: most of the time, that “Queued” status is exactly what Salesforce is supposed to show.
In my experience, this usually happens with jobs that were scheduled through the UI or via System.scheduleBatch without a specific end date. When you’re managing asynchronous Apex in Salesforce, understanding how the platform tracks these jobs is the difference between a quick check and a long night of unnecessary debugging.
Why your Salesforce batch job queued status is misleading
So, why does it stay in that status? When you schedule a batch job to run indefinitely, Salesforce creates a pointer in the system. It marks the job as “Queued” in the AsyncApexJob table to show that it’s waiting for its next scheduled time. It stays that way until the job actually fires or the schedule expires.
If you’re looking for details on a specific run, you might try running a query like this:
SELECT ApexClass.Name,
Id,
JobItemsProcessed,
JobType,
Status,
NumberOfErrors,
CreatedDate,
CompletedDate
FROM AsyncApexJob
WHERE ApexClass.Name = 'YourBatchClassName'
ORDER BY CreatedDate DESCBut if you see a Salesforce batch job queued here and the CreatedDate is from three days ago, don’t assume it hasn’t run since then. That row often represents the “schedule” itself, not the individual execution that happened this morning. Honestly, this is one of the most confusing parts of the Salesforce UI for newer developers.
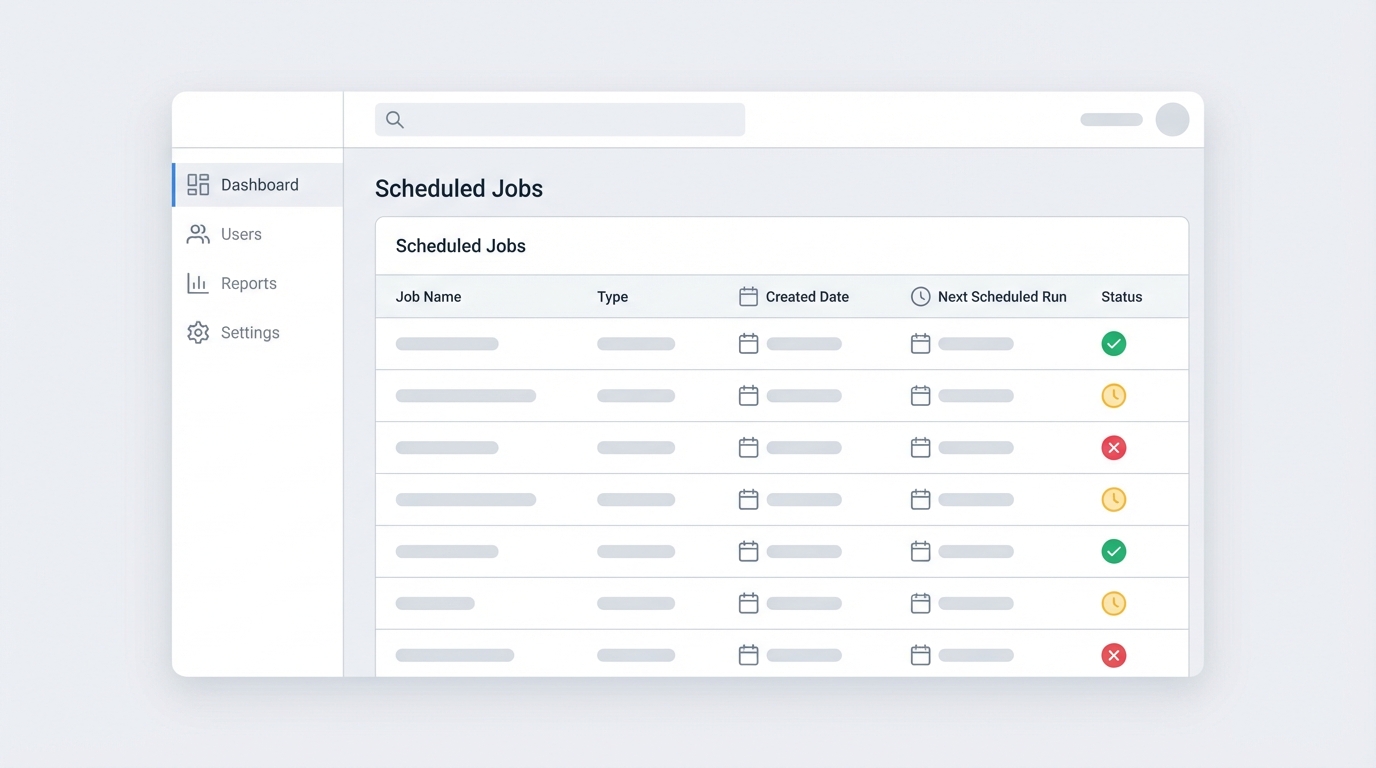
Using CronTrigger to solve the Salesforce batch job queued mystery
If you want to know when your job actually ran last, you have to look at the CronTrigger object. This is the source of truth for anything on a schedule. While AsyncApexJob tells you what happened during the execution, CronTrigger tells you if the engine is actually turning.
SELECT Id,
CronJobDetail.Name,
NextFireTime,
PreviousFireTime,
State
FROM CronTrigger
WHERE CronJobDetail.Name = 'YourScheduledJobName'Look at the PreviousFireTime. If that timestamp matches your expected schedule, your job is running fine, even if the other table still says the Salesforce batch job queued status is active. It’s also a good idea to keep an eye on your asynchronous Apex limits to make sure you aren’t hitting any walls that would prevent the next run from starting.
Pro tip: When you schedule a job, give it a clear, unique name. If you just call it “Daily Batch,” you’ll have a nightmare of a time finding it in the CronTrigger table if you have multiple classes running on similar schedules.
How to fix a Salesforce batch job queued indefinitely
If you really want to avoid that confusing “Queued” state in your logs, the fix is simple: always set an end date. When a scheduled job has a defined end point, Salesforce handles the status updates more cleanly. But let’s be real, most of us need these jobs to run forever. In those cases, you just have to get comfortable with the “Queued” status being the norm.
- Check CronTrigger to see the
NextFireTime. - Check AsyncApexJob only for errors and the number of items processed.
- Use a custom logging object in your
finish()method. This is a lifesaver. If you log every time a job completes, you don’t have to rely on Salesforce’s system tables at all.
Key Takeaways
- A Salesforce batch job queued status is often normal for jobs without an end date.
- The AsyncApexJob table can be misleading; it often shows the status of the schedule, not the last run.
- Always query CronTrigger to verify
PreviousFireTimeandNextFireTime. - Implement a custom logging framework to track batch success and failure reliably.
Next time you see that “Queued” status, don’t jump straight to aborting the job and rescheduling it. Run those two queries first. Most of the time, you’ll find everything is running exactly as it should, and you can get back to building things that actually need your attention.








Leave a Reply