What are the different Salesforce sandbox types?
If you’ve spent any time at all in an org, you know the first rule of the trail is never build in production, which is exactly why we need to talk about Salesforce sandbox types. Think of a sandbox as your private playground. It’s a safe place where you can break things, write messy code, and try out new flows without getting a frantic call from the VP of Sales because their reports stopped working.
But here’s the thing: not all sandboxes are created equal. I’ve seen teams struggle because they tried to do full-scale integration testing in a tiny Developer box, or they wasted a Full sandbox refresh on a minor CSS tweak. Let’s break down the four main options so you don’t make those same mistakes.
1. Developer Sandbox
This is the workhorse for most of us. It’s a copy of your production metadata – that’s your objects, code, and layouts – but it doesn’t bring any of your actual customer data over. It’s small, it’s free with most editions, and you can refresh it every day. I usually use these for my initial “can I even build this?” phase or for isolated unit testing.
2. Developer Pro Sandbox
Honestly, this is the “middle child” of the bunch. It’s still just metadata, but it gives you more storage for data you create yourself. If you’re building a complex LWC and need to load in a few thousand dummy records to see how it performs, this is where you do it. It’s also great for small team integrations where you need a bit more breathing room than the standard Dev box offers.
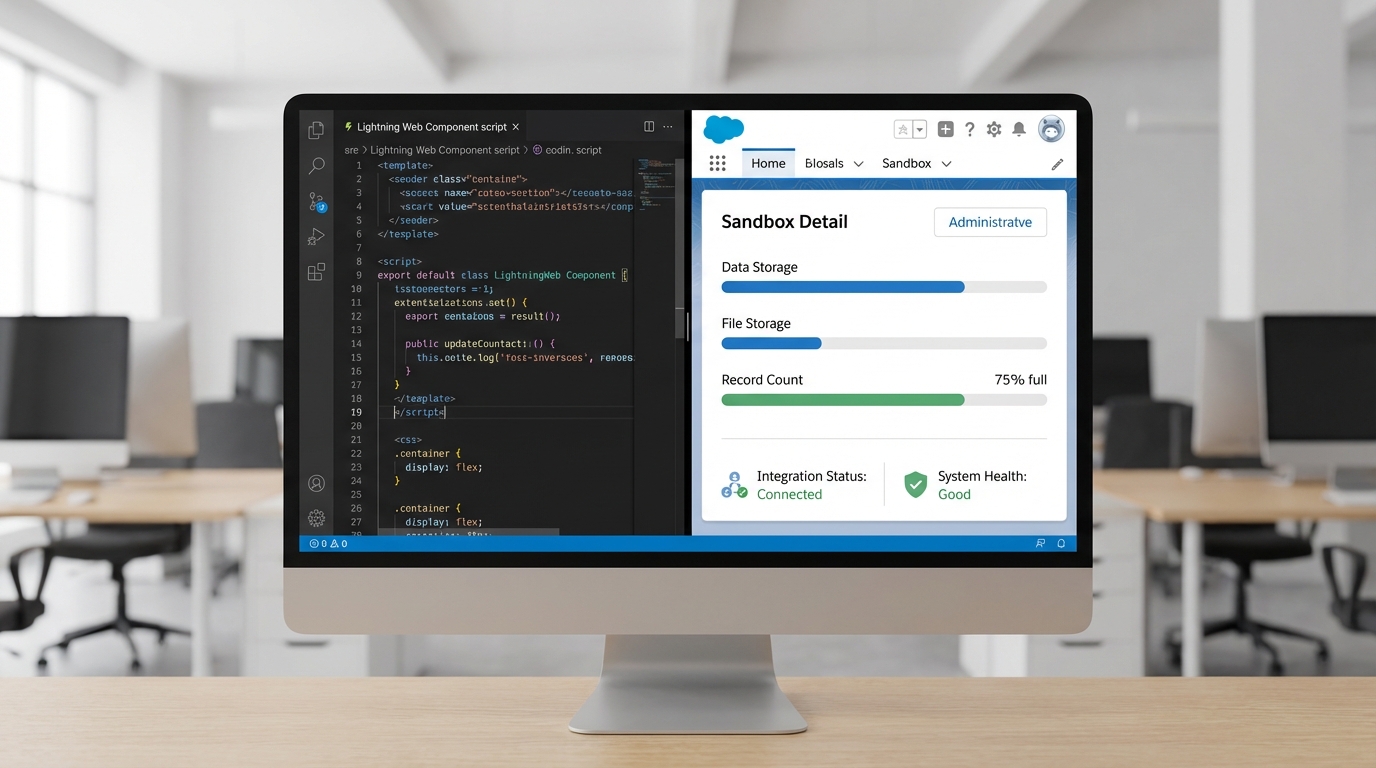
3. Partial Copy Sandbox
Now we’re getting into the good stuff. A Partial Copy sandbox includes your metadata plus a sample of your production data. You use a “sandbox template” to tell Salesforce exactly which objects you want to bring over. In my experience, this is the sweet spot for User Acceptance Testing (UAT). Users want to see data that looks familiar, not just “Test Account 123,” to feel comfortable signing off on a feature.
4. Full Sandbox
This is the big guns. It’s a 1:1 replica of your entire production environment – data, metadata, the whole lot. Because it’s so massive, you can usually only refresh it once every 29 days. This is where you do your final staging and performance testing. If you’re managing Salesforce large data volumes, you absolutely need a Full sandbox to see how your queries hold up under real pressure.
Quick tip: Never use your Full sandbox for day-to-day development. Since the refresh cycle is so long, you’ll end up stuck with “stale” metadata if you aren’t careful with your deployment pipeline. Use it for final validation only.
How to choose between Salesforce sandbox types for your project
So how do you actually pick? It usually comes down to three things: what are you testing, how much data do you need, and how often do you need to reset? If you’re just fixing a bug in an Apex trigger, a Developer sandbox is plenty. But if you’re testing a massive data migration, you’d be crazy not to use a Full or at least a Partial Copy.
One thing that trips people up is the refresh interval. I’ve seen developers get halfway through a project only to realize they need fresh data, but they’re stuck waiting three weeks for their next Full refresh. It’s a nightmare. Always plan your Salesforce sandbox types based on your release calendar. If you’re worried about losing work during a refresh, check out this guide on Salesforce sandbox recovery for some peace of mind.
Common Post-Refresh Tasks
- Email Deliverability: It’s set to “System Email Only” by default. If your testing involves sending emails to users, you’ll need to flip that to “All Email.”
- Integration Endpoints: Your sandbox will still try to talk to production external systems unless you go in and change the URLs in your Named Credentials or Remote Site Settings.
- User Data: Salesforce appends the sandbox name to usernames (e.g., [email protected]). Don’t forget this when you’re trying to log in for the first time!
- Masking: For Full sandboxes, make sure you’re using Salesforce Data Mask to hide sensitive PII so your devs aren’t seeing real customer credit card numbers or phone numbers.
Key Takeaways: Understanding Salesforce sandbox types
- Developer: Best for individual coding and unit tests. Metadata only. Refresh daily.
- Developer Pro: Good for heavier dev work and small team integrations. Metadata only but higher storage. Refresh daily.
- Partial Copy: The go-to for UAT and QA. Includes a sample of real data via templates. Refresh every 5 days.
- Full: The final staging area. Exact copy of production. Refresh every 29 days.
Look, the reality is that most of us work with whatever our company’s license allows. But if you have the choice, use the smallest sandbox possible for the task at hand. It keeps your dev cycle fast and saves the “heavy” environments for when they actually matter. So, next time you’re starting a new feature, take five minutes to think about which of the Salesforce sandbox types actually fits the bill. It’ll save you a massive headache down the road.








Leave a Reply