I’ve spent years cleaning up messy data, but using a Salesforce AI Flow to handle unstructured text is a total shift in how we work. We’ve all seen those customer emails that are just a wall of text with three different requests buried in the middle. Usually, an admin or a rep has to sit there and manually type that info into different fields. It’s a waste of time and honestly, it’s where most data entry errors happen.
Why a Salesforce AI Flow beats manual entry
Look, the old way of handling “messy” data involved complex Regex or just giving up and making it a manual task. But with an AI-powered flow, you can actually teach Salesforce to read. By using Agentforce actions inside your automation, you can pull out dates, quantities, and specific product names without writing a single line of Apex. I’ve seen teams cut down their processing time from minutes to seconds just by letting the AI do the heavy lifting of “reading” the message first.
So why does this matter? It’s about getting rid of that “swivel-chair” work. If you’re interested in other ways to use this tech, check out these 8 Practical Agentforce Use Cases for Salesforce Developers. It’s not just about orders; it’s about making the CRM actually understand what humans are saying.
The core pieces you’ll need
- Agentforce Agent – This is the “brain.” You’ll give it instructions on how to parse data and what actions to take.
- Screen Flow – This is your interface. It collects the text and shows the results to a person for a quick sanity check.
- Autolaunched Flows – These are the “hands.” They do the actual work like looking up a Contact or creating an Order record.
- Structured Outputs – This is how the AI talks back to the Flow. You define exactly what fields you want, like “Quantity” or “DeliveryDate.”
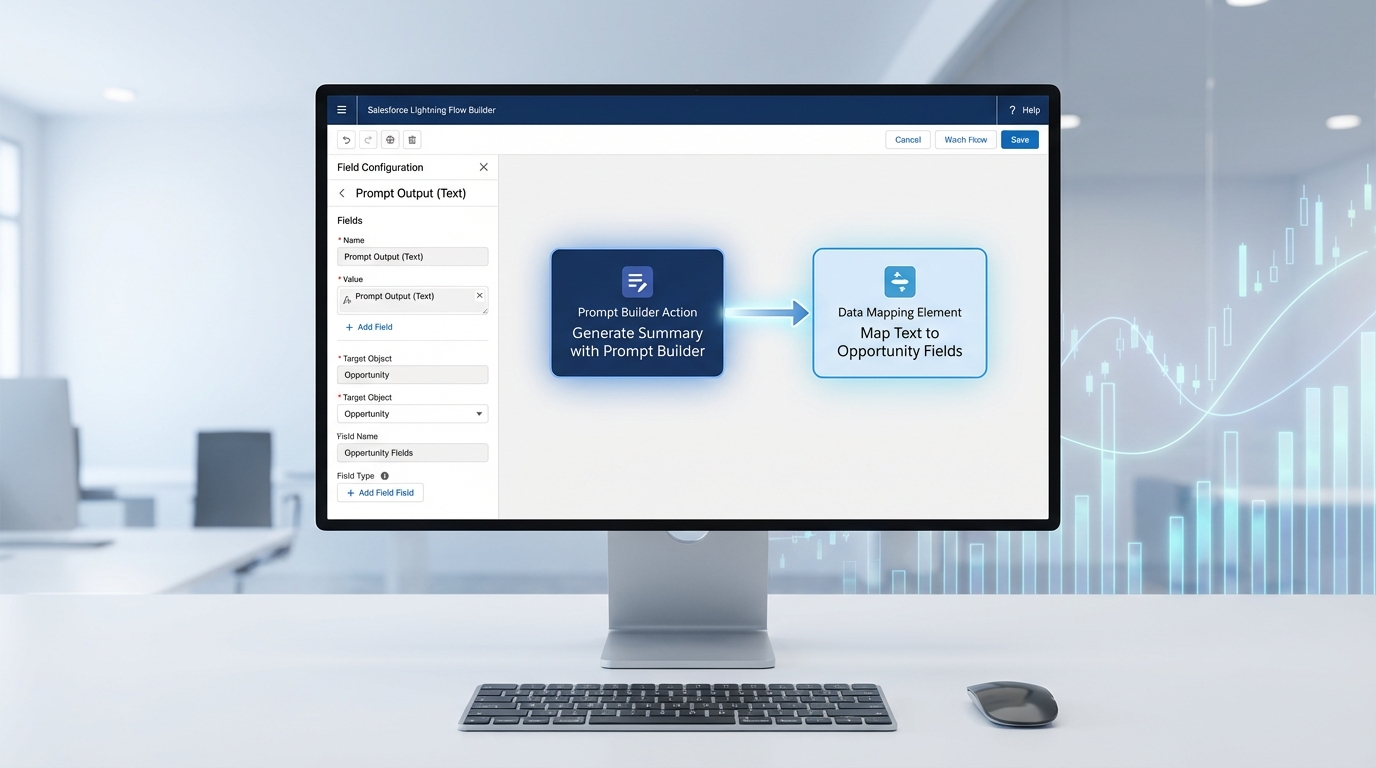
Setting up your first Salesforce AI Flow
Here is how I usually approach this. Don’t try to build the whole thing at once. Start by getting the AI to just recognize the data correctly, then add the record creation logic later. One thing that trips people up is being too vague with instructions. If you want a date in a specific format, tell the agent exactly that.
Step 1: Build the Agent and define the mission
Create your agent and give it a clear topic, like “Parse Order Details.” You need to be prescriptive here. Tell it: “If the user doesn’t specify a year, assume it is the current year.” These little details save you from a lot of headache during testing. You can also look into what RAG is in Salesforce to understand how grounding your agent in real data makes it even smarter.
Step 2: Map out your structured outputs
This is probably the most important part. You have to tell the AI exactly what you expect back. If you need a number, define it as a number. If it’s a list of items, tell it to format it as a string list. This makes it easy for your Flow to grab those values and put them into screen components or record variables.
Step 3: Create your helper flows
I like to keep my flows small and single-purpose. Create one autolaunched flow that just finds a Contact ID based on an email. Create another that just creates the Order. This makes troubleshooting way easier. If something breaks, you know exactly which “hand” isn’t working.
Step 4: Connect it all in a Screen Flow
Now, you’ll need a screen flow to host your Salesforce AI Flow logic. Start with a text area for the raw message. Then, call your Agentforce action. Once the agent returns the structured data, show it on a review screen. This “human-in-the-loop” step is vital. You don’t want the AI creating records blindly until you’re 100% sure it’s hitting the mark.
“Always show the parsed data to a user before hitting the ‘Save’ button. AI is smart, but a human catch on a weird typo is still the best safety net you have.”
Step 5: Test and tweak the instructions
You’ll find that the first time you run it, the AI might get a quantity wrong or miss a special instruction. Don’t panic. Just go back to your agent instructions and add a clarifying sentence. This is much easier than debugging 200 lines of code. For general tips on keeping your automation clean, these best practices for Salesforce Flow are a great place to start.
Best practices for real-world projects
In my experience, the biggest mistake people make is not passing the session ID. If you want the agent to remember what it just did in the previous step, you have to pass that sessionId variable along. Otherwise, it’s like the agent has amnesia every time a new action starts.
Also, keep your instructions deterministic. Instead of saying “be helpful,” say “always format dates as YYYY-MM-DD.” The more specific you are, the more reliable your Salesforce AI Flow will be. And honestly, most teams get this wrong by trying to make the agent too “conversational” when they really just need it to be a data extractor.
Key Takeaways
- Human-in-the-loop is non-negotiable – Always let a person verify the AI’s work before records are created.
- Small flows are better – Break your record creation into tiny, reusable autolaunched flows.
- Be specific – AI needs clear rules for dates, numbers, and priorities to avoid “hallucinations.”
- Context matters – Use session IDs to keep the conversation thread alive between different flow elements.
- Start simple – Get the parsing right before you try to automate the entire enterprise supply chain.
Building a Salesforce AI Flow isn’t just about following the latest trend. It’s about solving that age-old problem of turning messy human communication into clean, usable data. It takes a bit of trial and error to get the instructions perfect, but once it’s running, you’ll wonder how you ever lived without it. Start with one small use case-maybe just extracting a phone number or a date-and grow from there.








1 Comment