What is a Salesforce Queue and why should you care?
Ever had a client ask why they can’t just assign every new lead to a single person? We’ve all been there. A Salesforce Queue is basically a digital holding pen for records that haven’t found a permanent home yet. It’s one of those foundational tools that keeps a busy org from turning into a total mess by letting a team share the workload without records falling through the cracks.
Think of it as a bucket. Instead of a record sitting on one person’s desk while they’re out on vacation, it sits in the bucket where anyone on the team can grab it. It’s simple, but if you don’t set it up right, it can lead to some serious ownership confusion. Let’s break down how to use a Salesforce Queue the right way.
When you should actually use a Salesforce Queue
You don’t need a queue for everything. But if you have a group of people who all do the same job – like a support desk or a sales dev team – a queue is your best friend. I’ve seen teams try to manage this by manually reassigning records all day. Honestly, that’s just a waste of time.
Here are the common spots where a queue makes sense:
- New Leads: When leads come in from a web form and need to be claimed by the first available SDR.
- Support Cases: A tier-1 support team triaging incoming tickets.
- Operations Tasks: Records that need a “ready for review” status before a human takes over.
- Custom Objects: Any custom process where a team owns the work before an individual does.
But here’s the thing: a queue is about ownership. If you just want people to be able to see records, you’re looking for sharing rules, not a queue. Don’t mix the two up or your security model will get messy fast.
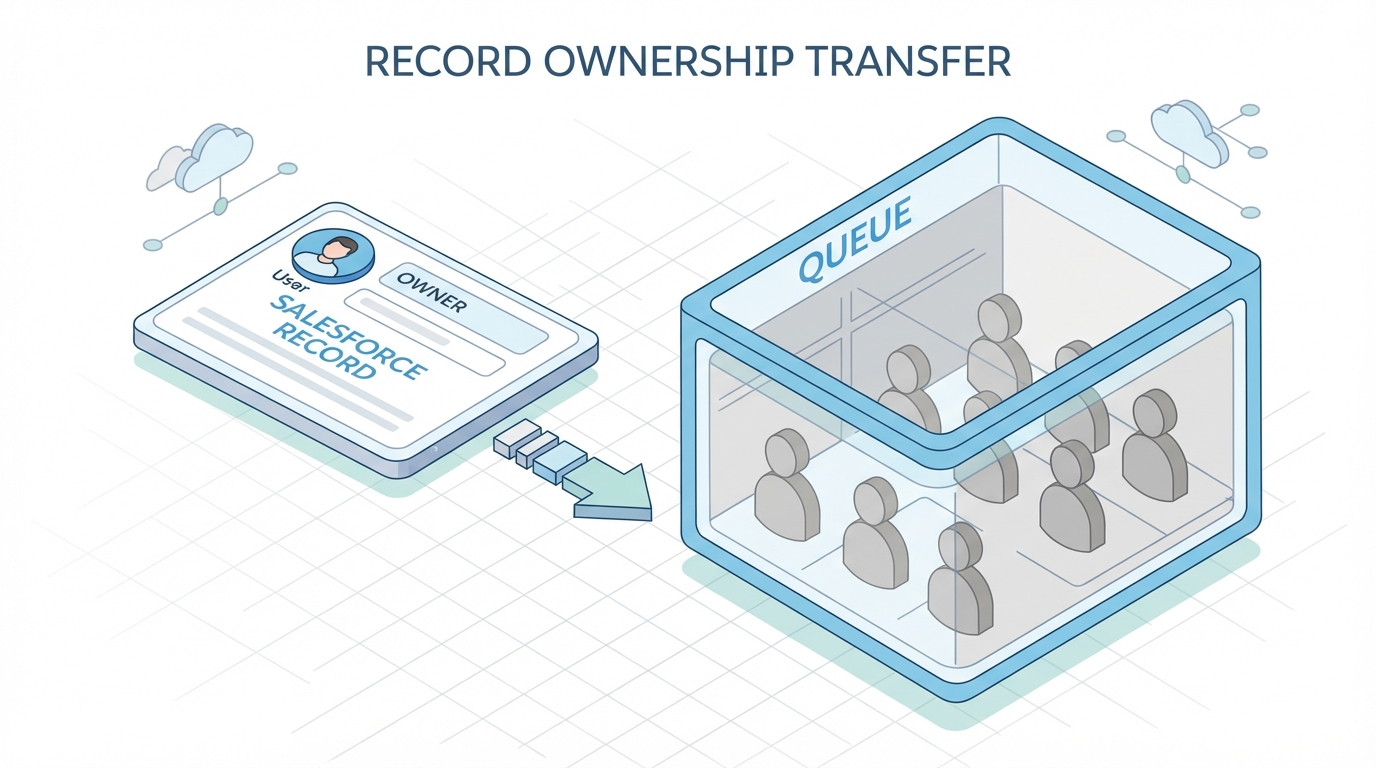
The technical bits of a Salesforce Queue
So what makes a queue tick? In the database, a queue is actually a record in the Group object. When a record is “in” a queue, the OwnerId field on that record is set to the ID of that Queue Group. It’s a bit of a shift if you’re used to records always being owned by a User, but it works perfectly with most automation.
Queue vs Public Group
This is a classic point of confusion for new admins. Both hold users, but they do different things. A Public Group is for sharing and visibility. A Salesforce Queue is for ownership. You can’t assign a Lead to a Public Group, but you can definitely assign it to a Queue.
How to get it running
Setting one up is straightforward. Head to Setup, search for Queues, and hit New. You’ll pick your members – which can be individual users, roles, or even public groups. The most important part? You have to choose which objects the queue supports. If you don’t check the “Case” box, you won’t be able to send cases to that queue. Simple, right?
Working with a Salesforce Queue in Code
If you’re a developer, you’ll eventually need to query or assign these via Apex or SOQL. Since queues live in the Group table, you have to filter by the ‘Queue’ type. I’ve seen people forget this and accidentally try to assign records to a regular Public Group, which throws an error every time.
Querying a Queue
// Find your queue by developer name
Group supportQueue = [SELECT Id FROM Group WHERE Type = 'Queue' AND DeveloperName = 'Support_Tier_1' LIMIT 1];
Assigning a record in Apex
When you’re writing triggers or services, you just treat the Queue ID like a User ID. Whether you’re deciding between Apex vs Flow for your automation, the logic remains the same: update the OwnerId.
// Quick example of assigning a new case to a queue
Case newTicket = new Case(
Subject = 'Printer is on fire',
OwnerId = supportQueue.Id
);
insert newTicket;
Best practices from the field
I’ve worked in orgs with hundreds of queues, and things can get ugly if you don’t have a plan. Here’s how to keep it clean:
- Naming is everything: Don’t just call it “Queue 1”. Use something like “US – Sales Leads” so people know exactly what’s inside.
- Clean up your members: If someone leaves the company, get them out of the queue. Better yet, use Roles or Public Groups as queue members so you don’t have to update the queue every time someone gets hired.
- Watch the volume: If a queue has 5,000 unassigned leads, your team isn’t using it – they’re ignoring it. Use list views to keep an eye on the “backlog” size.
Pro tip: Always enable the “Send Email to Members” option cautiously. If you have 50 people in a queue and it gets 100 leads a day, you’re just spamming your team. Use it for low-volume, high-priority queues only.
Key Takeaways
- A Salesforce Queue acts as a temporary owner for records like Leads and Cases.
- Queues are stored in the Group object with a Type of ‘Queue’.
- Unlike Public Groups, Queues can actually own records.
- You must enable specific objects for each queue in the Setup menu.
- Use assignment rules or Flow to route records to queues automatically.
At the end of the day, a Salesforce Queue is about making sure work gets done. It moves the focus from “who owns this?” to “is this work finished?”. If you’re building for a team that needs to collaborate on a pile of incoming records, a queue is almost always the right answer. Just keep your naming conventions tight and your membership lists updated, and you’ll be fine.








Leave a Reply