How to handle Salesforce integration interview questions like a pro
If you’re prepping for a technical role, you’ll definitely run into Salesforce integration interview questions. It’s one of those topics that separates the junior devs from the senior architects. At its heart, integration is just making two or more systems talk to each other so they can share data. Whether it’s an ERP, a marketing tool, or a legacy database, the goal is to stop people from having to type the same data into two different screens.
In my experience, the biggest mistake people make during interviews is getting too caught up in the code. Look, the code matters, but the interviewer wants to know if you understand the “why” and the “how” of moving data safely. You need to show that you can think about things like data consistency and what happens when a system goes offline. It’s not just about hitting an endpoint; it’s about building something that won’t break the first time there’s a network hiccup.
Common Salesforce integration interview questions and patterns
When you’re answering Salesforce integration interview questions, you have to talk about patterns. You don’t use the same tool for every job. If you try to use a real-time API for a million records, you’re going to have a bad time. Here’s how I usually break down the main patterns for teams I work with:
- Real-time Synchronous: This is for when you need an answer right now. Think of a credit card check or a real-time price lookup. You use REST or SOAP APIs here.
- Asynchronous (Batch): Use this when you have a lot of data and it doesn’t matter if it takes a few minutes or hours. The Bulk API is your best friend here.
- Event-driven: This is for when you want systems to react to changes. I’m a big fan of Platform Events and Change Data Capture (CDC) because they help keep systems decoupled.
- Middleware: If the logic gets too messy, you bring in the big guns like MuleSoft or Boomi. This is great for when you need to transform data or route it to five different places at once.
One thing that trips people up is choosing between different protocols. If you’re asked about the specifics, check out this guide on SOAP vs REST to get your definitions straight. It’s a classic interview topic.
Technical concepts for Salesforce integration interview questions
To really nail those Salesforce integration interview questions, you need to know the toolbox. Salesforce gives us a lot of built-in features so we don’t have to reinvent the wheel every time. I’ve seen teams waste weeks building custom listeners when they could have just used a standard feature. Here are the heavy hitters you should mention:
- REST and SOAP APIs: The bread and butter of most integrations. REST is usually the go-to because it’s lighter and uses JSON.
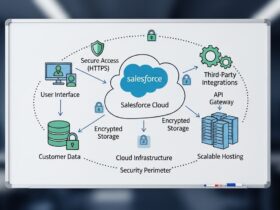
- Apex Callouts: This is how we push data out from Salesforce using code. Just remember you can’t do a callout if you have uncommitted work in the same transaction.
- Named Credentials: Honestly, this is the most overlooked security feature. It handles your authentication and headers so you don’t have to hardcode secrets. It’s much safer and easier to manage.
- External Services: This is a great “low-code” way to bring an outside API into Flow without writing a single line of Apex.
Example: A simple Apex HTTP Callout
Sometimes an interviewer will ask you to whiteboard a quick callout. You don’t need to be perfect, but you should show the basic flow. Here’s a quick snippet of what that looks like in the real world:
Http http = new Http();
HttpRequest req = new HttpRequest();
req.setEndpoint('callout:MyNamedCredential/v1/data');
req.setMethod('POST');
req.setHeader('Content-Type', 'application/json');
req.setBody('{"status": "active"}');
HttpResponse res = http.send(req);
if (res.getStatusCode() == 200) {
// This is where you'd process the response
}If you’re dealing with massive amounts of information, you’ll want to talk about managing large data volumes. Interviewers love to ask how you’d handle 10 million records without hitting governor limits.
Challenges you’ll actually face
Most Salesforce integration interview questions will eventually move toward “What could go wrong?” and that’s where your real-world experience counts. No integration is perfect. Systems go down, data gets messy, and tokens expire. You need to show you’ve thought about these scenarios.
Pro tip: Always mention error handling and logging. If an integration fails and there’s no log, you’re flying blind. I always suggest building a custom logging object or using a framework to track failures.
Authentication is another big one. Don’t just say “we use a password.” Talk about OAuth flows and JWT. If you want to sound like an expert, mention how you’d use the Salesforce JWT flow for secure server-to-server communication. It shows you care about security, not just getting the data to move.
Key Takeaways
- Pick the right pattern: Don’t use synchronous calls for big data loads. Use the Bulk API or batch jobs instead.
- Security first: Use Named Credentials and OAuth. Never hardcode usernames or passwords in your Apex classes.
- Think about limits: Always keep an eye on your API request limits and concurrent long-running request limits.
- Error handling is mandatory: Design your system to handle retries and log errors so you can fix things when they break.
- Keep it simple: Use standard features like External Services or Outbound Messages before jumping into custom code.
So, when you’re sitting in that interview chair, don’t just list features. Talk about the trade-offs. If they ask you why you’d choose one method over another, explain the impact on performance and maintenance. That’s what a senior professional does. Good luck with those Salesforce integration interview questions – you’ve got this.









Leave a Reply