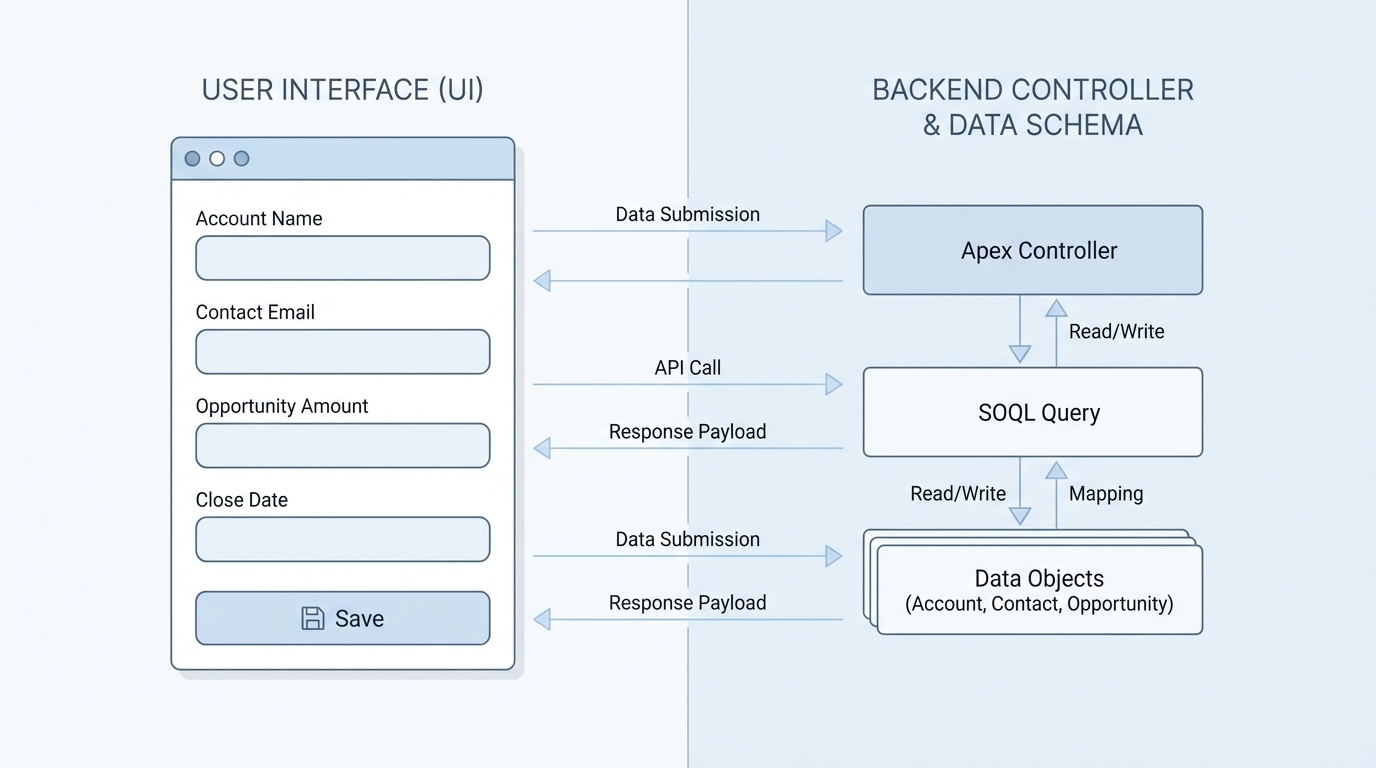
How Aura data binding actually works
If you’re still working in older orgs, understanding Aura data binding is a must-have skill for your toolkit. It’s basically the glue that connects your component attributes – the data model – to the markup that your users actually see. Without it, you’d be stuck doing manual DOM manipulation like it’s 2005, and nobody wants that.
In my experience, the easiest way to think about it is as a live link. When you use expression syntax like {!v.attributeName}, you’re telling Salesforce to keep the UI and the data in sync. But it’s not just about variables. You’re also using value providers like v for view attributes, c for your controller, and e for events. It’s a simple system, but it can get messy if you don’t respect the flow.
One thing that trips people up is the c provider. While v is for data, c is how you link your UI to your JavaScript logic. If you’ve ever wondered why do we use @AuraEnabled annotation?, it’s often because that’s the bridge between your client-side controller and the server-side data that eventually ends up in your bindings.
Choosing between one-way and two-way Aura data binding
Aura gives you a couple of ways to move data around, and honestly, most teams get this wrong by overcomplicating things. You have one-way (read-only) binding and two-way binding. The choice you make here affects how your app performs and how hard it is to debug later on.
One-way binding for simple displays
Use this when you just need to show a value. The markup reflects the attribute, but the view won’t change the data back. It’s clean and predictable. You’ll see this all the time with output components:
<lightning:formattedText value="{!v.title}" />The two-way binding trap
Now, here’s where it gets interesting. Aura supports two-way binding, which is great for inputs. If a parent component passes an attribute to a child, and that child updates it, the change flows back up. It sounds convenient, right? But I’ve seen teams build deep chains of two-way bindings that make it impossible to track where a bug actually started.
<! - Child component example - >
<aura:component>
<aura:attribute name="message" type="String" />
<ui:inputText value="{!v.message}" />
</aura:component>Look, if you’re building something complex, you’re usually better off looking at how LWC component communication works for inspiration. Even in Aura, moving toward explicit events instead of relying on two-way binding chains will save you a lot of headaches during code reviews.
Practical tip: If you find yourself passing the same attribute through three or more levels of components just to update a single value, stop. Use a component event instead. Your future self will thank you.
Communication and events
So what does this actually mean for your architecture? While Aura data binding is great for simple stuff, you’ll need events for the heavy lifting. You’ve got component events that bubble up and application events that broadcast to everyone. And if a parent needs to reach down and trigger something, you can always use cmp.find('child').someMethod(). It’s about using the right tool for the job.
Key Takeaways
- Aura data binding connects your attributes (v) to your markup using expression syntax.
- Value providers like
v,c, andeare the foundation of every Aura component. - One-way binding is safer for performance and keeping your data flow predictable.
- Two-way binding is handy for inputs but can become a “spaghetti code” nightmare in large hierarchies.
- Always favor explicit events for complex data updates between parent and child components.
At the end of the day, keep your bindings minimal. Every single binding adds a bit of overhead to the rendering engine. If you keep your data flow clear and use events when things get complicated, your components will stay fast and easy to manage. Just because you can bind everything doesn’t mean you should.









Leave a Reply