Choosing the Right Salesforce Report Types for Your Org
Choosing the right Salesforce report types is one of those foundational skills that sounds easy until you’re staring at a blank screen with a stakeholder breathing down your neck. I’ve spent years fixing reports that were built the wrong way, and it usually comes down to picking a format that doesn’t scale as the data grows. If you want to build dashboards that actually tell a story, you need to know which tool to grab from the toolbox.
Look, we’ve all been there. You build a quick list, and three weeks later, the VP of Sales asks for a chart and a breakdown by region. Suddenly, your simple list doesn’t work anymore. Understanding how these formats behave will save you from having to rebuild everything from scratch. Let’s break down how this actually works in the real world.
Breaking Down the Four Salesforce Report Types
Salesforce gives us four main ways to look at data. Each one has a specific job to do. Don’t try to force a tabular report to do a matrix report’s job – it just won’t end well.
1. Tabular Reports
Think of this as your basic Excel spreadsheet. It’s just a list of records with no groupings. I mostly use these when I just need to export data or check a quick list of “My Open Tasks” or “Active Users.”
But here’s the catch: you can’t use tabular reports to build dashboard charts unless you limit the rows. If you need to see totals or see data grouped by a specific field, you’re going to need something more flexible.
2. Summary Reports
This is the workhorse of the ecosystem. Most of the Salesforce report types you’ll build are going to be summary reports. They allow you to group rows of data. For example, you can group all your Opportunities by “Stage” or “Account Owner.”
This is the format you need if you want to see subtotals or create charts for a dashboard. In my experience, if you’re not sure which type to pick, start with a summary report. It’s the most versatile option for 90% of business requests.
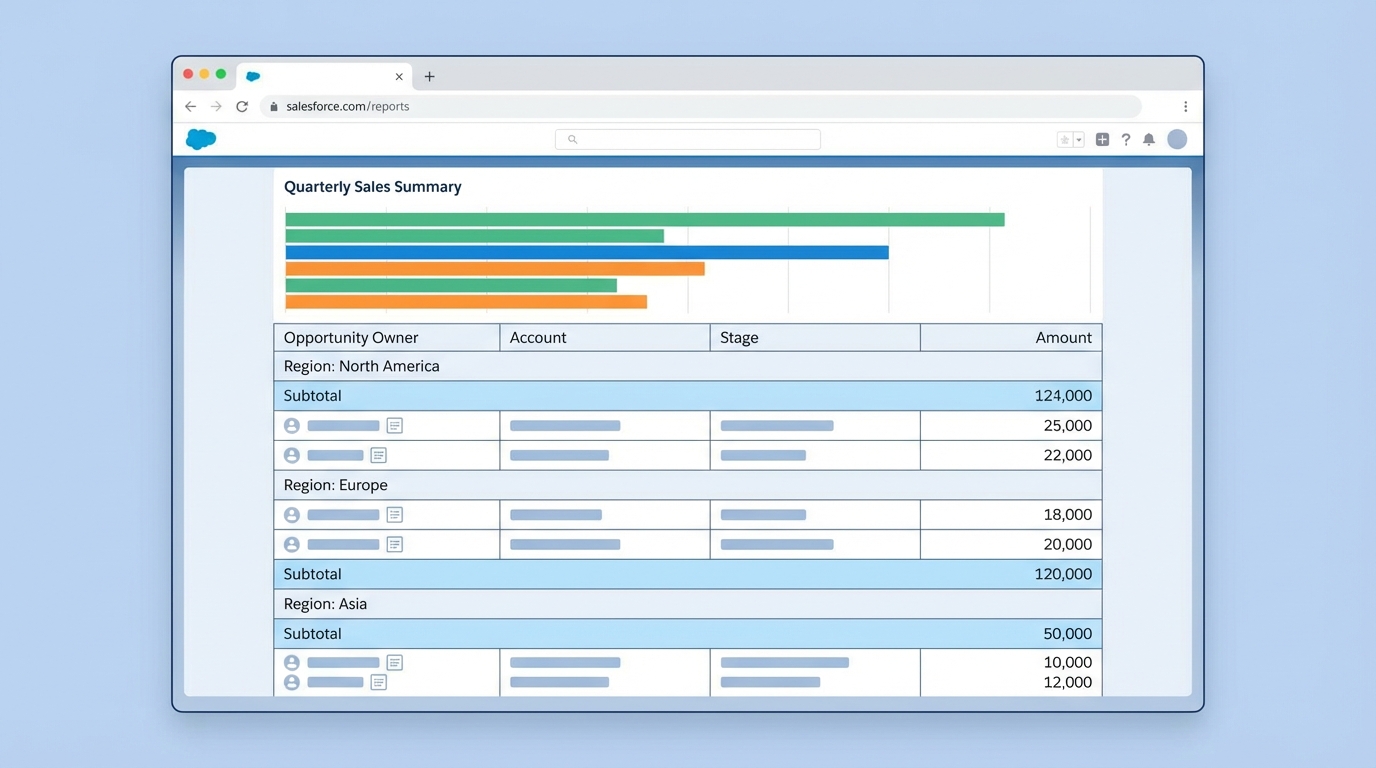
3. Matrix Reports
Matrix reports are for when you need to compare data across two different dimensions. You’re grouping by both rows and columns. It’s basically a pivot table within Salesforce. I usually use these for things like “Revenue by Month (Columns) and Product Category (Rows).”
They can be a bit harder to read at a glance, but they’re incredibly powerful for spotting trends over time across different segments. Just keep an eye on your filters; if you’re dealing with large data volumes, matrix reports can sometimes get a little sluggish if they’re too broad.
4. Joined Reports
I’ll be honest: most admins avoid joined reports because they look a bit intimidating. But they’re a lifesaver when you need to see two different types of information side-by-side. You can have one block showing “Sales Rep Quotas” and another block showing “Closed Won Deals” for that same rep.
Pro Tip: Joined reports are the only way to show data from different report types in a single view. If a stakeholder wants to see “Leads” and “Opportunities” in one report, this is your only path forward without building a crazy custom object.
Why Custom Salesforce Report Types Matter
Standard report types are great for basic stuff, but they often fall short when you have complex data relationships. This is where custom report types come in. They let you define exactly which objects and fields are available to your users. You should definitely check out this guide on standard vs custom report types to see when it’s time to build your own.
One thing that trips people up is the “with or without” relationship. If you use a standard report for “Accounts with Contacts,” you won’t see any Accounts that don’t have a Contact. If you need to see every Account regardless of whether they have a Contact, you have to build a custom report type with “A may or may not have B” logic.
Advanced Reporting Features to Keep in Your Back Pocket
- Bucket Fields: These are great for when you need to group values on the fly without asking a dev to create a new field. Think “Small, Medium, Large” based on deal size.
- Cross Filters: Want to see “Accounts without any Cases”? Cross filters are the easiest way to do this without writing a single line of code.
- Row-Level Formulas: I use these all the time for quick math, like calculating the number of days between two dates right on the report.
Running Reports via the API
Sometimes you need to get this data out of Salesforce programmatically. If you’re a dev, you’ll likely use the Analytics REST API. It’s pretty straightforward. You just hit the report endpoint with a GET request:
GET /services/data/v62.0/analytics/reports/{reportId}This returns a JSON blob of all your data and groupings. It’s much cleaner than trying to scrape the UI or running heavy SOQL queries for complex aggregations. I’ve used this to feed custom LWC components when the standard report charts weren’t enough.
Key Takeaways
- Use Tabular for simple lists and data exports.
- Use Summary for most dashboard charts and grouping data by one field.
- Use Matrix for two-dimensional comparisons (like a pivot table).
- Use Joined to compare different datasets (like Leads vs. Accounts) in one view.
- Always consider Custom Report Types if the standard ones are hiding records you need to see.
At the end of the day, the best report is the one that actually gets used. Don’t over-complicate things just because you can. Start with the simplest format that answers the business question. If you find yourself building the same report over and over with slight variations, it might be time to look into dynamic filters or even AI-driven insights to help your users find what they need faster. Keep it clean, keep it fast, and your users will thank you.








Leave a Reply