If you are looking to set up a Shopify Salesforce integration, you are likely tired of chasing down order numbers across two different systems. I have seen so many teams struggle with data drift because their store and their CRM just aren’t talking to each other. Here is the thing: a good Shopify Salesforce integration isn’t just about moving data-it is about making sure your sales and service teams actually trust what they see on the screen. When your data is synced correctly, you stop guessing and start actually using your customer history to drive more sales.
Why bother with a Shopify Salesforce integration?
When these two systems talk, life gets a lot easier for everyone. Your marketing team can see exactly what people are buying without asking for a CSV export, and your support team can see order statuses right inside the Service Console. I’ve worked on projects where the finance team was spending ten hours a week just matching up Shopify payouts to Salesforce records. That is time they could have spent on actual analysis. By centralizing orders, customer history, and inventory, you create a single source of truth that stays accurate as you scale.
What to do before you start your Shopify Salesforce integration
I cannot stress this enough: don’t just start mapping fields on day one. You need a plan. One thing that trips people up is trying to sync every single field available. Trust me, you don’t need all 50+ Shopify metadata tags in Salesforce. It just creates noise. Here is a quick checklist of what I usually look at before we touch any code or tools:
- Pick your data: Decide if you really need inventory and returns, or if just customers and orders will do for now.
- Clean your data: If you have “John Doe” in Shopify and “J. Doe” in Salesforce, you are going to have a bad time. Merge your duplicates first.
- Standardize SKUs: Make sure your product codes match across both platforms. If they don’t, your order sync will fail.
- Check API limits: Shopify has rate limits, and so does Salesforce. If you are doing a massive initial sync, you need to account for this.
- Security: Create a dedicated integration user in Salesforce. Don’t use your own admin account. It makes troubleshooting and auditing so much easier later on.
Pro Tip: When you set up your integration user, give it the least amount of permission it needs to do the job. I’ve seen integrations accidentally wipe out custom field data because the permissions were too broad.
Pick your integration approach
There isn’t a one-size-fits-all way to do this. The right choice depends on your budget and how much custom logic you have. If you are just starting out, a pre-built connector might be fine. They are usually cheaper and get you running in hours. But if you have complex rules-like custom subscription logic or multi-currency setups-you might need something more flexible.
For mid-sized companies, middleware like Workato or MuleSoft is often the sweet spot. It lets you build logic without writing a ton of Apex. However, if you are dealing with massive scale or very specific business rules, a custom Salesforce API integration is usually the best bet. It costs more upfront but won’t break when your business grows.
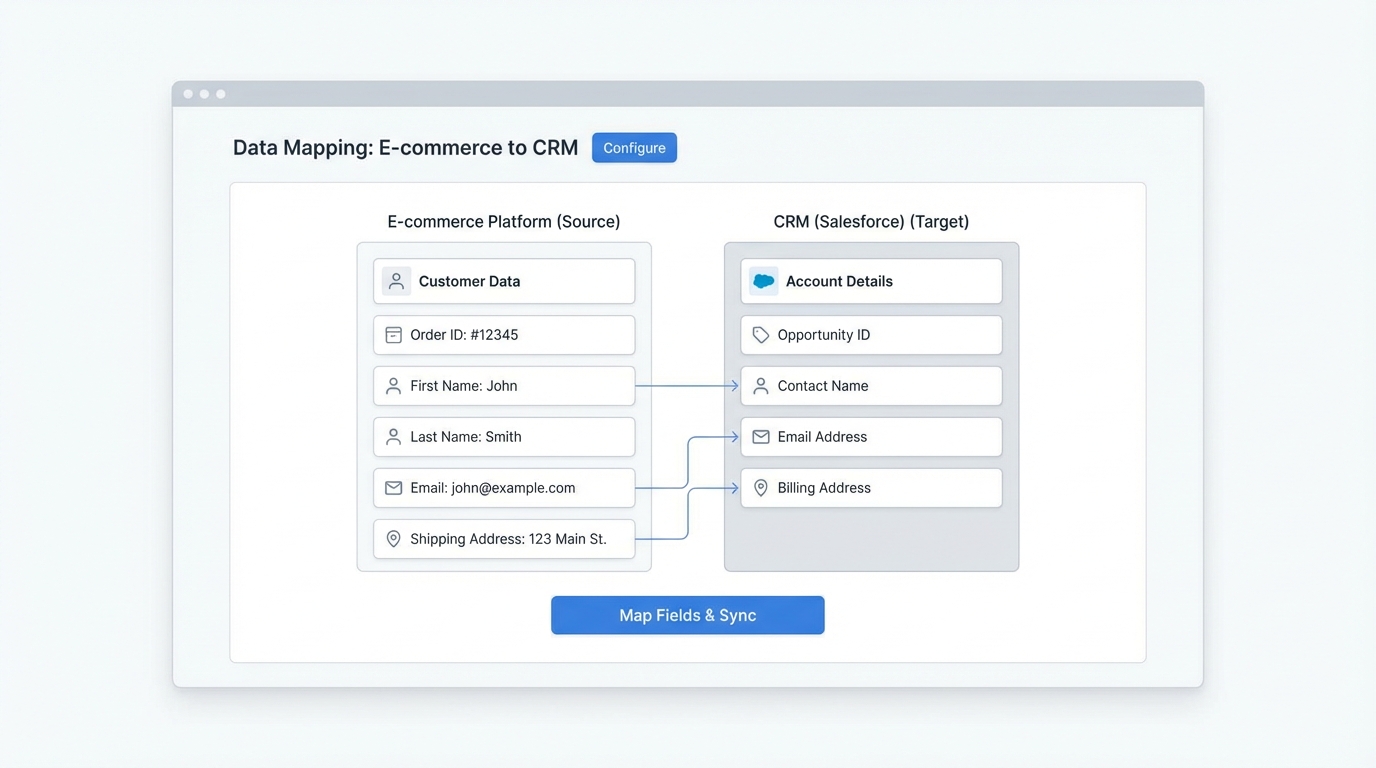
Building your Shopify Salesforce integration step by step
- Map your fields: Get a spreadsheet and map every Shopify field to a Salesforce field. Be careful with picklists. If a value exists in Shopify but not in Salesforce, the sync will error out.
- Set up the pipe: Connect your systems and define how often they sync. Is it real-time? Every hour? For most teams, a 5-15 minute delay is perfectly fine and saves on API calls.
- Test the weird stuff: Don’t just test a standard order. Test a partial refund. Test a discount code that brings the total to zero. Test a split shipment. These “edge cases” are where most integrations fail.
- Phase the rollout: Don’t flip the switch for your entire store at once. Start with one region or a small group of customers. Watch the logs for a few days to make sure nothing is breaking.
- Train the humans: Your team needs to know where to find the data. Show them where the “Shopify Order Number” lives in Salesforce and how to tell if a sync has happened.
Mistakes I’ve seen teams make (and how to avoid them)
One of the biggest mistakes is not defining “ownership.” If a customer changes their email in Salesforce, does that update Shopify? Or does Shopify always win? If you don’t decide this early, you’ll end up with data bouncing back and forth in a loop. Also, please don’t ignore error handling. You need a way to get notified if the sync stops working. There is nothing worse than realizing a week later that 500 orders never made it into Salesforce.
If you are dealing with a high volume of transactions, you also need to be careful about managing large data volumes. Salesforce can slow down if you are dumping millions of order line items into it without a strategy for archiving or indexing. Keep your org lean by only syncing what you actually need for reporting and service.
Key Takeaways
- Clean your data before you start-garbage in means garbage out.
- Start small and sync only the essential fields to reduce noise.
- Always test edge cases like refunds and partial cancellations.
- Set up automated alerts so you know the second a sync fails.
- Decide which system “owns” the data to avoid sync loops.
At the end of the day, a Shopify Salesforce integration should be something you set up and then forget about. It should just work in the background. If you find yourself constantly fixing sync errors, it is usually a sign that your data mapping or your error handling needs another look. Take the time to do the boring prep work now, and you’ll save yourself a lot of late-night troubleshooting later.








Leave a Reply