If you are trying to wrap your head around the differences between IaaS PaaS SaaS, you have probably run into a wall of technical jargon that makes it sound way more complicated than it actually is. In my experience, the easiest way to think about the cloud is just using someone else’s computer over the internet so you do not have to buy or manage the physical hardware yourself. It is that simple.
Making Sense of IaaS PaaS SaaS in the Real World
I remember the first project where we moved off-premise. We were tired of waiting six weeks for the procurement team to rack a new server just to test a small integration. With the cloud, we did it in five minutes. That speed is exactly why companies are obsessed with it. You get servers, storage, and databases on demand, and you only pay for what you actually use.
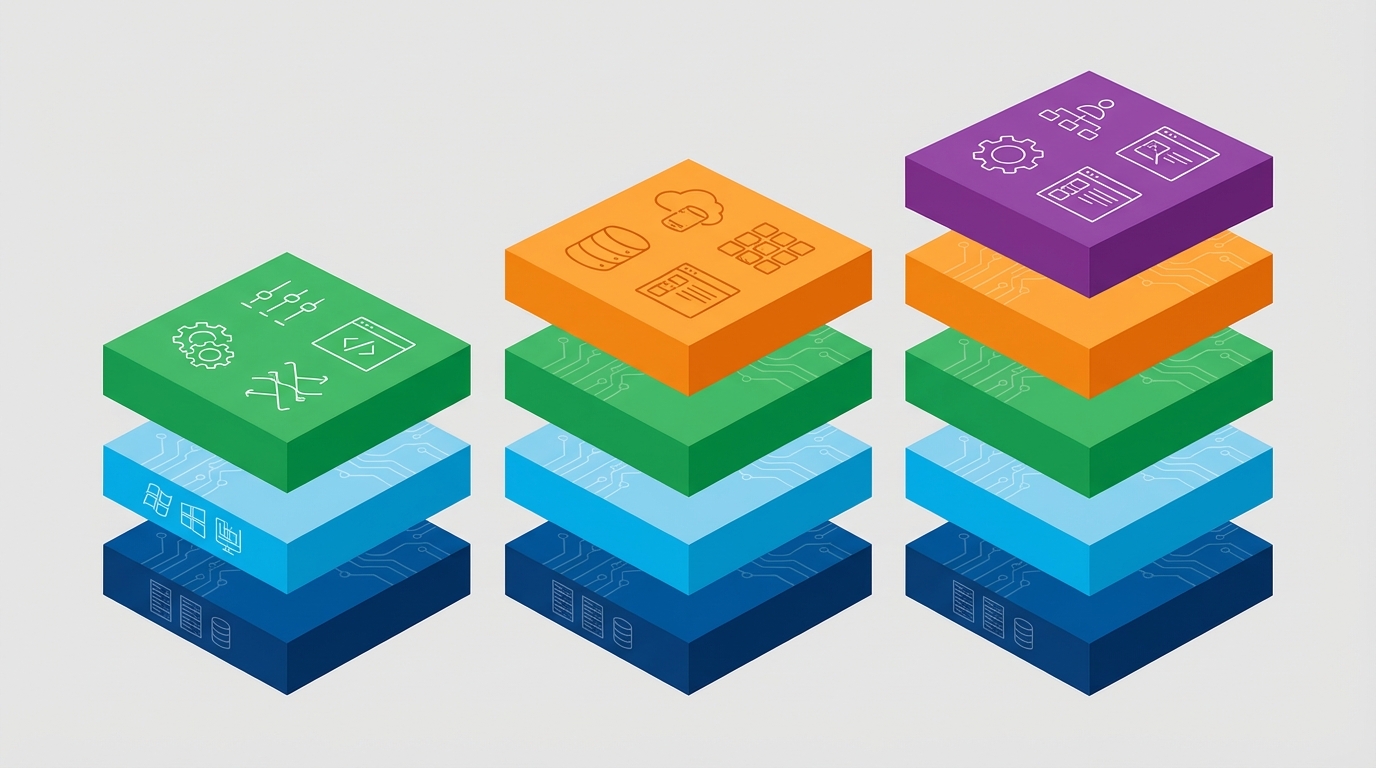
When we talk about the fundamentals of IaaS PaaS SaaS, we are really talking about how much of the “stack” you want to manage. Look, some people want to build the whole car, and some people just want to call an Uber. Both are valid, but you need to know which one you are signing up for before you start billing the client.
The Three Models You Will Actually Use
This is where things usually get a bit blurry for folks. I have seen plenty of developers get these mixed up in interviews. The short answer? It is all about how much of the work you want to do yourself. Let’s break this down.
- IaaS (Infrastructure as a Service): This is the raw stuff. You are renting the virtual hardware. If you want to know more about the nitty-gritty of the hardware side, check out this guide on what IaaS actually is.
- PaaS (Platform as a Service): This is for the builders. You do not care about the OS or the hardware; you just want to push your code and have it run. You can read more about how PaaS works here.
- SaaS (Software as a Service): This is what most of us use every day. Think Salesforce or Gmail. You just log in and use the app. If you are curious about the business side, here is a deep dive into SaaS explained.

Choosing Between IaaS PaaS SaaS for Your Project
So where does this stuff actually sit? Most of the time, you will be on a Public Cloud like AWS or Azure. It is cheap and it works. But I have worked with banks that would not touch a public cloud with a ten-foot pole, so they build a Private Cloud in their own data center. Honestly, most big companies end up with a Hybrid Cloud nowadays.
They keep the super sensitive stuff on their own servers and put the web apps on the public cloud. It sounds great on paper, but it can be a real headache to manage if the integration isn’t solid. And then there is Multi-cloud, which is just using different providers so you are not stuck with just one. It is a lot to juggle, but it prevents vendor lock-in.
Pro tip: When you are talking about IaaS PaaS SaaS in an interview, do not just recite definitions. Talk about a time the cloud helped you solve a real business problem, like scaling a database during a holiday sale. That is what actually gets you hired.
Here is the thing: most people think the cloud provider handles all the security. That is a huge mistake. It is a shared responsibility. The provider secures the physical building and the hypervisor, but you are still responsible for your data and who has access to it. I have seen teams get into real trouble because they left an S3 bucket open to the public or forgot to set up proper permissions.

Key Takeaways
- IaaS gives you the most control but requires the most maintenance.
- PaaS lets you focus on code without worrying about servers.
- SaaS is ready to use out of the box with zero management.
- The IaaS PaaS SaaS choice depends entirely on your team’s skills and budget.
- Security is always a shared responsibility – never assume the provider has it all covered.
Look at this quick example of how easy it is to start a server using a command line. You do not need to be a hardware expert to do this anymore:
aws ec2 run-instances - image-id ami-0123456789abcdef0 - count 1 - instance-type t3.microOne command and you have a server running. That is the power of the IaaS PaaS SaaS ecosystem. But remember, once it is running, you are paying for it. So do not forget to turn it off when you are done testing. I have seen more than one “free” project turn into a $500 bill because someone left an instance running over the weekend.








3 Comments