Why You Need to Care About Salesforce Sandbox Types
If you’ve spent more than five minutes in the ecosystem, you know that testing in production is the fastest way to lose your weekend. That’s where understanding the different Salesforce Sandbox types comes in. I’ve worked on projects where we tried to squeeze a massive integration test into a tiny Developer sandbox, and let me tell you, it wasn’t pretty. You need the right tool for the job if you want to keep your production data clean and your users happy.
Think of a sandbox as your playground. It’s a safe place to break things, build new features, and try out that crazy new automation without worrying about breaking the live system. But not all playgrounds are built the same. Some are just a small sandbox in a backyard, while others are full-scale theme parks. Choosing the right one depends entirely on what you’re trying to build.
Breaking Down the 4 Salesforce Sandbox Types
Salesforce gives us four main options. Each one has its own storage limits, refresh rates, and price points. While all Salesforce Sandbox types share the same metadata – things like your custom objects, fields, and code – the real difference is how much actual data they can hold.
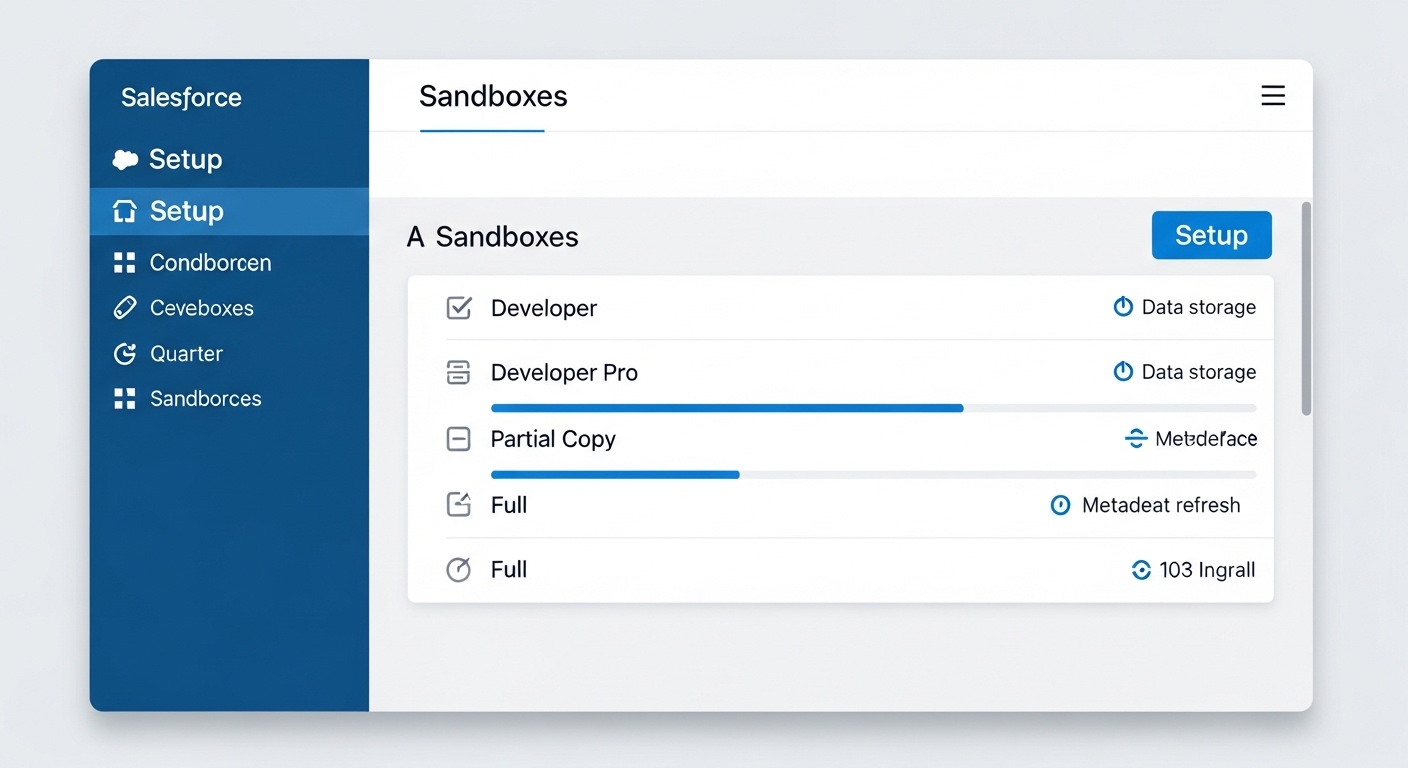
1. Developer Sandbox
This is the entry-level option. It’s great for individual developers who just need a place to write code or build a few flows. You get all the configuration from production, but basically zero data. It’s small, it’s fast to create, and you can refresh it every day. I usually tell my teams to use these for “unit testing” – just making sure the logic works before moving it up the chain.
2. Developer Pro Sandbox
Think of this as the Developer sandbox’s older sibling. It still doesn’t come with your production data, but it has much higher storage limits. This is where I like to do integration testing. If you need to connect to an external system and push a bunch of test records through, the standard Developer sandbox will run out of space fast. Developer Pro gives you that extra breathing room.
3. Partial Copy Sandbox
Now we’re getting into the good stuff. A Partial Copy sandbox includes a sample of your production data. You use a “sandbox template” to tell Salesforce exactly which objects you want to copy over. This is perfect for Quality Assurance (QA) or User Acceptance Testing (UAT). It feels real because the data is real, but you aren’t paying for a 1:1 replica of your entire database.
4. Full Sandbox
The Full sandbox is exactly what it sounds like – a total mirror of your production org. Metadata, records, attachments, the whole deal. These are expensive and they take a long time to refresh (usually once a month), but they’re essential for staging. If you’re about to push a massive release, you want to test it here first. It’s also the only place you should ever do performance or load testing.
One thing that trips people up is the refresh interval. I’ve seen developers accidentally refresh a sandbox that had weeks of uncommitted code in it. Always check with the team before hitting that button, and if you do run into trouble, check out this guide on recovering sandboxes to see what your options are.
Comparing Salesforce Sandbox Types for Your Team
So how do you decide? In my experience, most teams get this wrong by trying to save a buck on a Partial Copy when they really need a Full, or vice versa. Here’s a quick look at how the limits usually stack up. Keep in mind that your specific contract might change these numbers slightly.
| Feature | Developer | Developer Pro | Partial Copy | Full |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Refresh Interval | 1 Day | 1 Day | 5 Days | 29 Days |
| Data Storage | 200 MB | 1 GB | 5 GB | Same as Prod |
| Includes Data? | No | No | Sample (Template) | Everything |
Choosing Between Salesforce Sandbox Types
The choice between Salesforce Sandbox types usually comes down to your development lifecycle. If you’re just fixing a bug in an Apex trigger, a Developer sandbox is fine. But if you’re testing how a complex Flow handles thousands of records, you’ll want something with data. Speaking of Flows, make sure you’re following best practices for Salesforce Flow so your testing stays manageable across these environments.
But here’s the kicker: don’t forget about data security. Even though these are “test” environments, they often contain sensitive customer info if you’re using Partial or Full sandboxes. I always recommend using a data masking tool or manually scrambling sensitive fields after a refresh. Just because it’s a sandbox doesn’t mean you can ignore compliance.
Key Takeaways
- Developer/Pro: Use these for building and early testing. They’re cheap and fast.
- Partial Copy: Use this for UAT and training. It’s the best balance of cost and realism.
- Full: Use this for your final staging and performance checks. It’s your last line of defense.
- Templates: Don’t forget to set up templates for your Partial sandboxes or you’ll end up with no data.
- Refresh: Watch those clocks! A 29-day wait for a Full sandbox refresh can stall a project if you mistime it.
At the end of the day, mastering the various Salesforce Sandbox types is about risk management. You want to move fast, but you don’t want to break things. By picking the right environment for each stage of your project, you’ll spend less time fixing data issues and more time actually building cool stuff. Now, go check your Setup menu and see what you’ve got available – you might be surprised at what’s sitting there unused.








10 Comments