Getting LWC component communication right
One of the first things you’ll hit when building a custom UI is LWC component communication. I’ve seen plenty of developers overcomplicate this, but it really comes down to where your components sit in the DOM. If you don’t pick the right pattern, you’ll end up with a mess of spaghetti code that’s almost impossible to debug later. Sound familiar?
Look, we’ve all been there. You build a beautiful set of components, but then you realize they can’t actually talk to each other. Let’s break this down into the patterns that actually matter for your day-to-day work.
Passing data down with @api
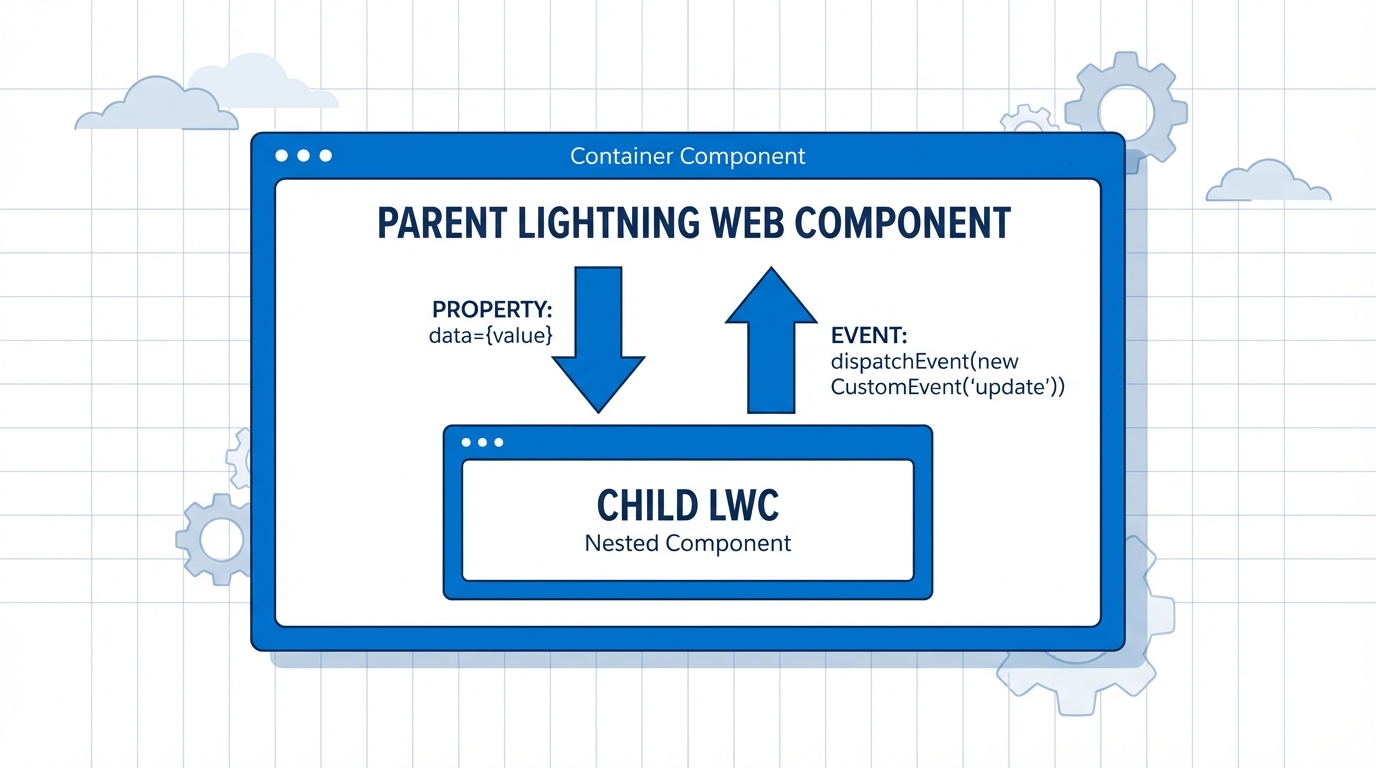
This is the bread and butter of LWC. If you’ve got a parent component that needs to tell a child what to do, you use a public property. Just mark the variable in the child with @api and you’re good to go. It’s the simplest way to handle one-way data flow.
// child.js
import { LightningElement, api } from 'lwc';
export default class ChildComponent extends LightningElement {
@api message;
}
In the parent, you just pass the value through the HTML attribute. It’s clean, and it keeps your data flow predictable. I always tell my team to stick to this whenever possible because it makes the component’s contract very clear. But remember, the child shouldn’t try to change this value directly – that’s the parent’s job.
Mastering LWC component communication for complex layouts
Now, what happens when the child needs to talk back? This is where things get interesting. You don’t want the child reaching into the parent’s logic. Instead, the child should just shout out that something happened and let the parent decide how to handle it. We do this with custom events.
Using Custom Events for child-to-parent talk
When a user clicks a button or finishes a task in a child component, you dispatch a CustomEvent. The parent listens for that event in its HTML template. It’s like the child is saying, “Hey, I’m done!” and the parent reacts.
In my experience, you should keep your event detail payloads as light as possible. If you’re passing huge objects around, you might want to rethink your data strategy. Usually, a record ID or a simple status string is all you really need.
If you’re building something complex, like a custom list with LWC element scrolling, events are how you tell the parent to load more data or update the UI state. It keeps the components independent, which is exactly what we want for reusability.
Lightning Message Service (LMS) for siblings
But what if the components aren’t related at all? Maybe they’re in different regions of the Lightning App Builder or even on different pages. You can’t use a simple event because there’s no common parent to listen for it. This is a classic LWC component communication challenge.
In the old days, we used a custom PubSub module, but honestly, you should just use LMS now. It’s the standard for communication when you’re working across different DOM trees or even with Aura components. Plus, with the new LWC expressions coming out, managing how components react to these messages is getting even easier.
// publisher.js
import { publish, MessageContext } from 'lightning/messageService';
import MY_CHANNEL from '@salesforce/messageChannel/MyChannel__c';
// Inside your class
@wire(MessageContext)
messageContext;
handleAction() {
const payload = { recordId: '123', status: 'success' };
publish(this.messageContext, MY_CHANNEL, payload);
}
Key Takeaways for LWC component communication
- Use @api for parent-to-child: It’s the most reliable way to pass data down.
- Use CustomEvents for child-to-parent: This keeps your child components decoupled and reusable.
- Use LMS for everything else: If components aren’t in a direct parent-child relationship, Lightning Message Service is your best friend.
- Keep it simple: Don’t use LMS for a simple parent-child link. It’s overkill and makes the code harder to follow.
- Watch your payloads: Only send the data that’s absolutely necessary to avoid performance lags.
Handling LWC component communication doesn’t have to be a headache. Start with the simplest pattern and only move to something like LMS when the component relationship requires it. Most of the time, a clean parent-child setup is all you need to get the job done. So, next time you’re architecting a new feature, ask yourself: “Does this component really need to know about its neighbor, or can a simple event do the trick?”








15 Comments